The circulatory systems is one of the most vital system in the human body. It is responsible for the transportation of blood, oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to all the organs and tissues, while also removing waste products and carbon dioxide. The circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
The Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest, slightly to the left. It acts as a pump, continuously contracting and relaxing to propel blood throughout the body. The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The atria receive blood from the veins, while the ventricles pump blood out through the arteries.
The heart’s contractions are controlled by electrical signals, ensuring that blood is pumped in a coordinated and efficient manner. The heart also has valves that prevent the backward flow of blood, ensuring that it flows in one direction.
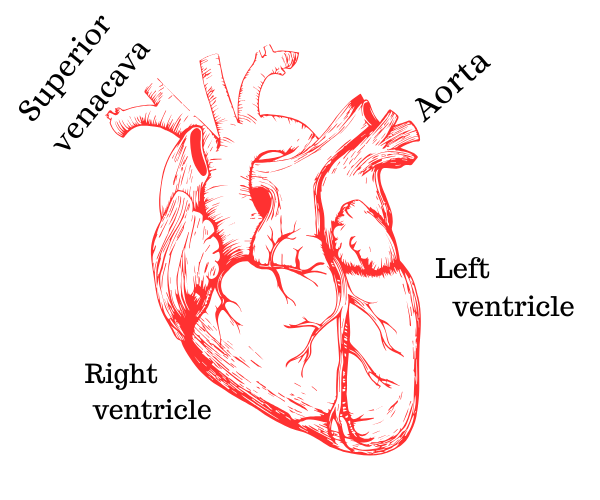
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are the network of tubes that transport blood throughout the body. There are three main types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the organs and tissues. They have thick, elastic walls that help maintain blood pressure and ensure a steady flow of blood.
Veins, on the other hand, carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. They have thinner walls compared to arteries and contain valves that prevent the backflow of blood.
Capillaries are tiny, thin-walled vessels that connect arteries and veins. They are responsible for the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and the surrounding tissues.
Blood
Blood is a specialized fluid that circulates through the circulatory system. It consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen to the body’s tissues. White blood cells are part of the immune system and help fight off infections and diseases. Platelets are responsible for blood clotting, preventing excessive bleeding.
Plasma is the liquid component of blood and contains various proteins, hormones, and nutrients. It also helps maintain the pH balance and temperature of the body.
Circulatory Systems Function
The circulatory system has several important functions:
- Transportation: It transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products to and from the body’s cells.
- Regulation: It helps regulate body temperature, pH balance, and electrolyte levels.
- Protection: It plays a crucial role in the immune response, helping to defend the body against infections and diseases.
Circulatory System Disorders
Various disorders can affect the circulatory system, including:
- Heart disease: This includes conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
- Hypertension: Also known as high blood pressure, it can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Stroke: It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, leading to brain damage.
- Peripheral artery disease: It affects the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, usually in the legs.
- Deep vein thrombosis: It is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, usually in the legs.
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent or manage circulatory system disorders.

Pingback: Blood vessels: types and their complete role - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Edema: An Expert View To Overcome Edema - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: White Blood Cells | Types and functions: - Pharmacyinfos