Definition:
Blood is one of the transport systems that transport essential nutrients and oxygen to various organs and eliminate carbon dioxide from the body. Blood is composed of platelets, plasma, Red Blood Cells (RBC), and White Blood Cells (WBC). Blood is pumped by the heart through the blood vessels. Blood is used to maintain homeostasis.
Components of blood:
Blood has formed by the following components,
Plasma,
Red Blood Cells (RBC),
White Blood Cells (WBC),
Platelets.
Plasma:
Plasma is the largest component in blood. It makes up about 55% of the overall content. This is mainly water with a wide range of substances dissolved or suspended in it.
Functions of plasma:
- Its main function is to transport essential nutrients, oxygen, hormones, and electrolytes to the various tissues and organs,
- And also redistributing the water to the body requirements,
- Maintain blood pressure and blood circulation.
Red Blood Cells (RBC):
It is otherwise called erythrocytes. The name erythrocyte is derived from the Greek word erythros means ‘red’ and kytos means ‘hollow vessel‘. RBC is the biconcave in shape. It is red due to the presence of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein used to carry oxygen and other nutrients. Hemoglobin levels vary from person to person. Men have higher levels of hemoglobin compared to women. Normal range of RBC for adults, the usual range is generally 4.35 to 5.65 million red blood cells per microliter (mcL) of blood for men and 3.92 to 5.13 million red blood cells per microliter (mcL) of blood for women.

Functions:
- Carry oxygen from lungs and deliver to all the tissues present in body. Oxygen (O2) get binds with Red Blood Cells due the presence of hemoglobin.
- It also carries carbon dioxide (CO2) from various tissues and excretes via the lungs through the exhale process.
White Blood Cells (WBC):
White Blood Cells are also called leukocytes. The name leukocyte is derived from the Greek word leuk means ‘white’, and cyte means ‘cell’. WBC‘s main role is to protect the body against microbes. WBC surrounds microbes and engulfs and destroys the foreign particles by phagocytosis mechanism. The normal range of WBC count for adults is about 4,500 to 11,000 WBC per microliter of blood.
Functions:
- They are kill the bacteria and microbes by phagocytic mechanism, because they are phagocytic in nature.
- Protect the body against allergic conditions and also kill the parasites that enter the body.
- WBC secrete and transport the serotonin, heparin and histamine.
Platelets:
Platelets are also called ‘thrombocytes’. The word thrombocytes is derived from the Greek word thrombos means ‘thick drop or clot’, and cyte means ‘cell’. Platelets form small fragments in the area of ruptured blood vessels. The normal range of platelets present in the blood is about 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Having more than 450,000 platelets is a condition called thrombocytosis. Having less than 150,000 platelets is a condition called thrombocytopenia.
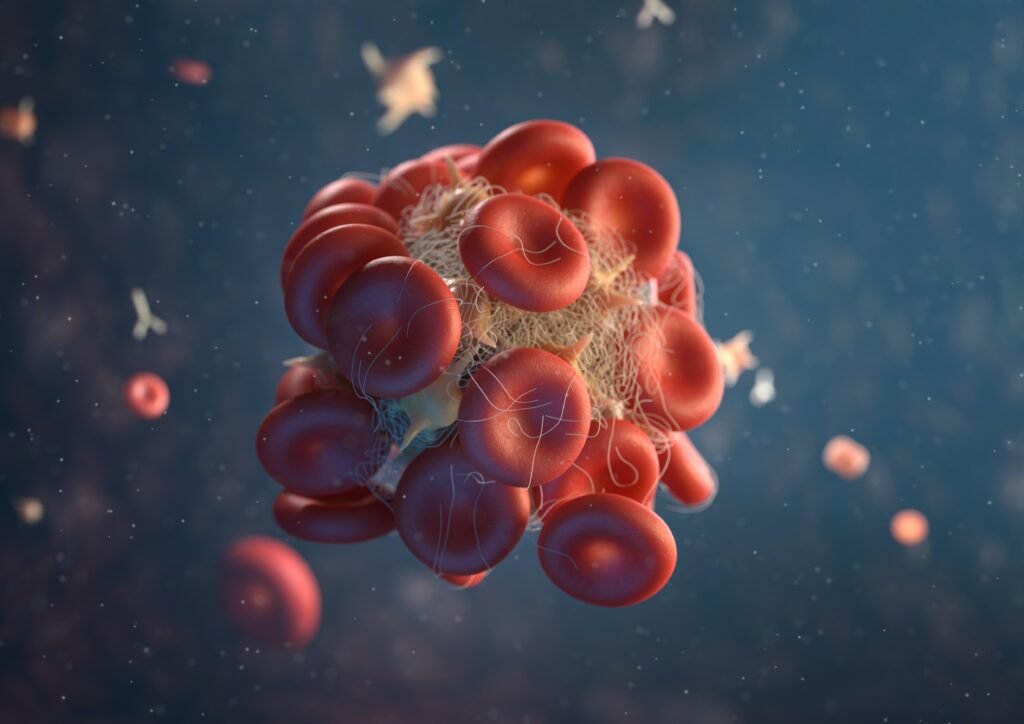
Functions:
- Its main function is to prevent blood loss from ruptured blood vessels by clot formation.

Pingback: What is positive feedback in homeostasis - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: What is negative feedback in homeostasis - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Red Blood Cells | Formation and Function: - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Circulatory Systems in the Human Body - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: White Blood Cells | Types and functions: - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: What are platelets?- Functions and diseases - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: What is anemia? and how to easily overcome it - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: The best diet plan for iron deficiency anemia - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Blood vessels: types and their complete role - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: What is atherosclerosis? and how to completely overcome it? - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Natural treatment for edema in legs and feet - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Pulmonary hypertension supportive therapy - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Brain Aneurysm Treatment Without Surgery - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Edema: An Expert View To Overcome Edema - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Calcium Channel Blockers Mechanism Of Action - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Nifedipine Mechanism Of Action - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Beta Blockers Mechanism Of Action - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Atenolol Mechanism Of Action - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Is Amlodipine Good For High Blood Pressure? - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Diuretics Mechanism Of Action - Pharmacyinfos
Pingback: Introduction To The Nervous System - Pharmacyinfos